How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly sought after. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced maneuvers and adhering to legal and ethical considerations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone flight, photography techniques, troubleshooting common issues, and responsible drone ownership. Prepare to take flight with confidence and knowledge.
From understanding the functions of propellers and flight controllers to navigating complex flight modes and capturing stunning aerial footage, this guide aims to equip you with the necessary skills to become a proficient drone pilot. We’ll cover essential safety protocols, legal requirements, and maintenance best practices to ensure your drone operations are both successful and responsible.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section provides a detailed overview of key drone parts and a glossary of common terms.
Drone Components and Their Functions

A drone’s functionality relies on the seamless integration of several key components. Let’s explore each one:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for flight. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of efficiency and performance.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Brushless motors are common due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, the flight controller is a small computer that manages all aspects of flight, receiving input from sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands.
- Battery: Provides the electrical power for all drone components. Battery life significantly impacts flight time.
- GPS Module (optional): Allows for precise positioning and navigation, enabling features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and waypoint navigation.
- Camera (optional): Captures aerial photos and videos. Features vary widely depending on the drone model.
- Gimbal (optional): A stabilized mount for the camera, ensuring smooth and shake-free footage, even during flight maneuvers.
- Radio Transmitter/Remote Controller: Allows the pilot to control the drone’s movements and functions.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terms will enhance your understanding of drone operation and maintenance.
- LiPo (Lithium Polymer): A common type of rechargeable battery used in drones.
- LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage): A higher-voltage version of LiPo batteries, offering increased flight time and power.
- mAh (milliampere-hour): A measure of battery capacity, indicating how long the battery can power the drone.
- C-Rating: Indicates the maximum discharge rate of a battery, influencing the power output.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor individually.
- RTH (Return-to-Home): A feature that allows the drone to automatically return to its takeoff point.
- FPV (First-Person View): A system that allows the pilot to see what the drone’s camera sees in real-time.
- Gimbal Lock: A situation where the gimbal’s movement is restricted, resulting in limited camera movement.
Drone Battery Comparison
Choosing the right battery is crucial for optimal flight performance. Here’s a comparison of common battery types:
| Battery Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo | High power density, lightweight | Requires careful handling, can overheat | Most drones |
| LiHV | Higher voltage, longer flight time | More expensive, requires compatible charger | High-performance drones |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for ensuring safe and responsible drone operation. This section Artikels essential steps and safety regulations.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously follow this checklist:
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage.
- Check the battery level and ensure it’s properly connected.
- Verify the propeller blades are securely fastened.
- Calibrate the compass and GPS (if applicable).
- Check the radio transmitter batteries and connection.
- Review the weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
- Confirm you have the necessary permissions and are operating within legal limits.
- Inform others nearby about your drone flight.
Safety Regulations and Guidelines
Adhering to safety regulations and best practices is crucial for responsible drone operation. Always comply with local laws and regulations regarding drone usage. Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times. Avoid flying near airports, crowds, or restricted airspace. Be mindful of privacy concerns and avoid flying over private property without permission.
Safe Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart, How to operate a drone
A visual representation of the pre-flight inspection process helps ensure no step is missed. (A detailed flowchart would be included here, illustrating the steps Artikeld above in a sequential flow.)
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoffs and landings are essential for preventing accidents and damage. This section details proper procedures and techniques.
Safe Takeoff Procedure
A smooth takeoff involves several key steps. Begin by placing the drone on a level surface. Power on the drone and transmitter. Ensure the GPS signal is locked (if applicable). Gently increase the throttle, allowing the drone to ascend smoothly and steadily.
Avoid abrupt movements.
Safe Landing Procedure
Landing requires a similar level of control and precision. Gradually lower the throttle as you approach the ground. Maintain a steady descent to avoid a hard landing. Choose a flat, clear landing area free from obstacles.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Various takeoff and landing techniques exist, depending on the drone and environmental conditions. Assisted takeoff utilizes automated features to simplify the process. Manual takeoff requires more pilot skill and control.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which provides comprehensive guidance. From there, practice and experience will refine your skills, allowing you to confidently operate a drone in various environments.
Controlling Drone Movement and Navigation
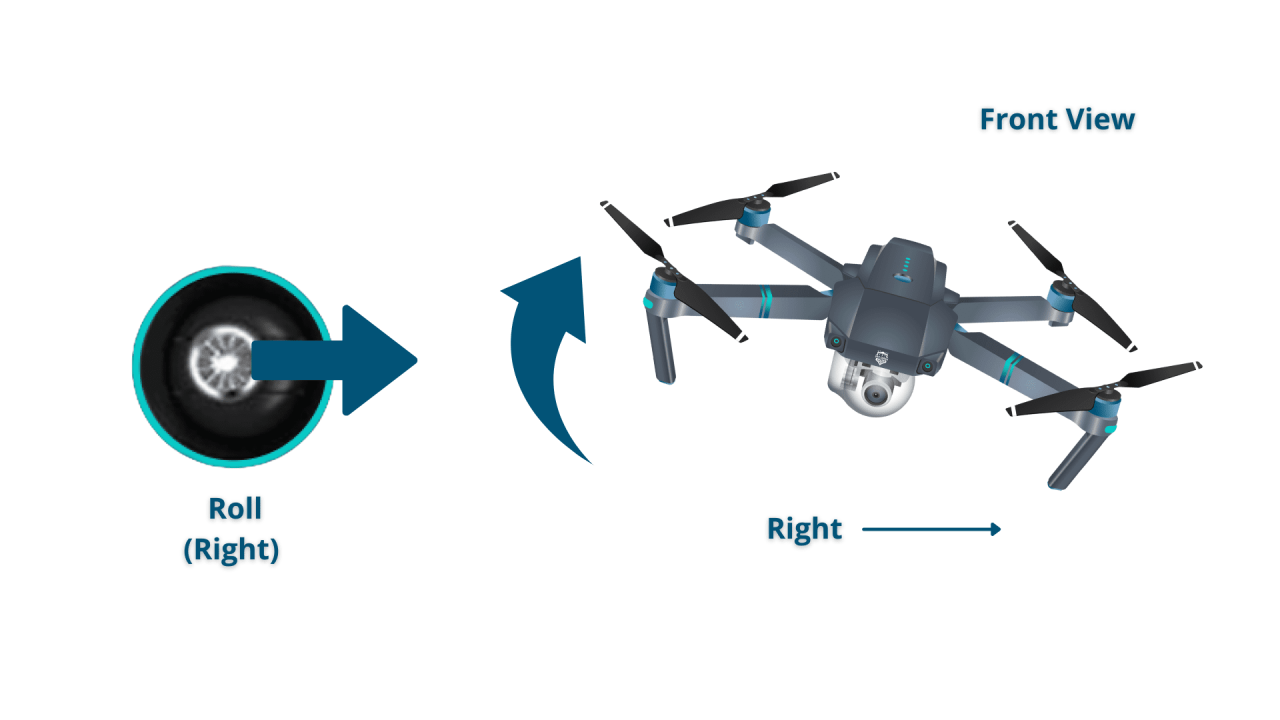
Mastering drone control is crucial for safe and efficient flight. This section explains how to use the controls to maneuver the drone and utilize navigational aids.
Drone Control Inputs
Most drones use joysticks on the remote controller for directional control. One joystick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the other controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right). Buttons on the controller often activate specific functions like Return-to-Home (RTH) or camera controls.
Flight Modes
Many drones offer various flight modes to cater to different skill levels and flight scenarios. Beginner modes often limit speed and responsiveness, while advanced modes provide greater control and maneuverability.
GPS and Navigation Aids
GPS provides precise location data, enabling features like RTH and waypoint navigation. Some drones incorporate additional sensors, such as obstacle avoidance systems, to enhance safety and navigation.
Photography and Videography with a Drone
Capturing stunning aerial photos and videos requires understanding camera settings and composition techniques. This section provides guidance on achieving high-quality results.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
To capture high-quality images and videos, consider factors like lighting, camera settings (ISO, shutter speed, aperture), and smooth flight maneuvers. Experiment with different settings to find the optimal balance for your environment and desired effect.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Understanding the impact of different camera settings is crucial for producing high-quality footage. Adjusting ISO affects sensitivity to light, while shutter speed controls motion blur and exposure. Aperture influences depth of field.
Tips for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Effective composition enhances the visual appeal of your aerial media. Consider the rule of thirds, leading lines, and framing to create visually engaging shots. Experiment with different angles and perspectives to capture unique and creative images.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
This section identifies common drone problems and provides solutions for resolving them. Proactive troubleshooting minimizes downtime and ensures smooth operation.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Various issues can arise during drone operation. Addressing them effectively requires understanding the cause and implementing appropriate solutions.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, high power consumption | Charge the battery fully, reduce flight time or power consumption |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructions, interference, weak signal | Fly in an open area, avoid interference sources, recalibrate GPS |
| Motor Failure | Motor damage, ESC malfunction | Inspect the motor and ESC, replace if necessary |
| Drone not responding to controller | Low transmitter battery, connection issues | Check and replace transmitter batteries, check controller and drone connection |
Drone Maintenance and Storage
Regular maintenance and proper storage significantly extend the lifespan of your drone and its components. This section details essential maintenance and storage practices.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule involves cleaning the drone body and propellers, inspecting for damage, and checking all connections. Frequency depends on usage, but regular checks are recommended.
Prolonging Battery Lifespan

Proper battery care is crucial for maximizing its lifespan. Avoid fully discharging or overcharging the battery. Store batteries in a cool, dry place, and avoid extreme temperatures.
Proper Storage
Store the drone and its accessories in a clean, dry, and protected environment. Avoid direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Use protective cases or bags to prevent damage during transport.
Advanced Drone Techniques
Once comfortable with basic operation, you can explore advanced flight maneuvers and features to enhance your drone’s capabilities.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers like flips, rolls, and precise hovering require significant practice and skill. Start slowly and gradually increase the complexity of your maneuvers as your skills improve. Always prioritize safety.
Advanced Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and automation. Understanding these modes allows you to adapt your flight style to different scenarios and enhance your drone’s performance.
Advanced Features
Features like waypoint navigation and obstacle avoidance enhance the drone’s capabilities and safety. Mastering these features opens up possibilities for more complex and autonomous flights.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Responsible drone operation involves adhering to legal regulations and ethical guidelines. This section highlights crucial legal and ethical considerations.
Drone Laws and Regulations
Laws and regulations regarding drone operation vary significantly depending on location. Before flying, research and understand the specific regulations in your area. Always comply with all applicable laws and obtain necessary permissions.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical drone operation involves respecting privacy, avoiding reckless behavior, and being mindful of the impact on others. Always prioritize safety and avoid any actions that could compromise the privacy or safety of others.
Ethical Guidelines for Drone Pilots
- Obtain necessary permissions before flying in restricted areas.
- Maintain visual line of sight with your drone.
- Respect the privacy of others and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Fly responsibly and avoid reckless behavior.
- Be aware of your surroundings and potential hazards.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of technical understanding, practical skills, and a commitment to responsible flying. This guide has provided a framework for safe and effective drone use, from pre-flight preparation to advanced flight techniques and ethical considerations. By understanding the mechanics, adhering to regulations, and continuously practicing, you can unlock the full potential of your drone and capture breathtaking aerial perspectives responsibly.
FAQs: How To Operate A Drone
What is the best type of drone for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with features like GPS stabilization and beginner modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good reviews and ease-of-use features.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
Compass calibration should be performed before each flight, especially if you’ve transported your drone or experienced any significant magnetic interference.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires a good grasp of the fundamentals, and a helpful resource for learning this is available at how to operate a drone. This guide covers everything from basic maneuvers to more advanced techniques, ensuring you’re well-prepared for safe and effective drone operation.
Proper training is crucial for responsible drone piloting.
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (if available) and carefully bring it back to your location, prioritizing safety.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and flight conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for an estimated flight time, and always have spare batteries available.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Consult your local aviation authority’s website or contact them directly for the most up-to-date regulations in your area. Websites like the FAA (in the US) are also good resources.
